
 |
|
|
Ultiquest Technology aslo fabricates and offer a avriety of crystal componensts with optical crystals.Crystals can be optically uniaxial or biaxial, depending on the regularity of the crystal structure, and it is often necessary to consider the axial directions of crystals.
Select the appropriate material for the application in question. Most optical crystal materials in current use are synthesized, except for those used as polarization elements, which are produced from calcite.
Crystal materials not shown in the table below may be available upon request. Please contact our engineer for more information. |
| |
 Calcium Fluoride Crystals (CaF2)-------------------------------- Calcium Fluoride Crystals (CaF2)-------------------------------- |
|
|
 Calcium Fluoride can be used in the ultraviolet, visible and infrared spectral regions. Calcium Fluoride has a
transmission above 90% between 0.25 and 7¦Ìm. Calcium Fluoride can be used in the ultraviolet, visible and infrared spectral regions. Calcium Fluoride has a
transmission above 90% between 0.25 and 7¦Ìm.
Calcium Fluoride is twice as hard as Barium Fluoride and also less usceptible to thermal shock. However, it is
commonly used in cryogenically cooled thermal imaging systems. It is less expensive than Barium Fluoride.
CaF2 is diamond turnable
|
|
| Property |
Specification |
| Transmission Range |
0.13¦Ìm to 7.0¦Ìm |
| Density |
3.18 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient |
18.85x10-6 / ¡ãC |
| Surface Finish |
Polishes of 20-10 scratch-dig are mostly specified for use in UV and visible
applications. Typical specifications for surface quality in the infrared are a
40-20 scratch dig in the 0.75 to 3¦Ìm spectral region and 60-40 scratch-dig for the
3-7¦Ìm area. |
| Surface Figure |
In the UV and Visible spectral regions, surface figure ranges from
1/10 wave to 1/4 wave @ 0.6328¦Ìm. In the infrared, typical required surface figure
ranges from 1/4 wave to 2 waves @ 0.6328 ¦Ìm and are specified depending on the
system performance requirements. |
| AR Coating Options |
Available coatings for CaF2 include BBAR for 0.8 to 2.5¦Ìm, 3 to 5¦Ìm or the 1 to 5¦Ìm
spectral regions |
| Typical Applications |
Cryogenically cooled thermal imaging, Astronomical, Microlithography, Excimer
Laser applications. |
| Products Manufactured |
Lenses, Aspheric lenses, windows, Optical Beamsplitters, Optical Filters,
Wedges, Prisms. |
|
|
|
|
|
 Optical
Transmittance Curve of CaF2 (Reference Data): Optical
Transmittance Curve of CaF2 (Reference Data): |
|
 |
|
|
|
 Germanium (Ge )------------------------------------- ----------- Germanium (Ge )------------------------------------- ----------- |
|
 Germanium has the highest index of refraction of any commonly used infrared transmitting materials. It is a
very popular material for systems operating in the 3-5 or 8-12¦Ìm spectral regions. Germanium blocks UV and Germanium has the highest index of refraction of any commonly used infrared transmitting materials. It is a
very popular material for systems operating in the 3-5 or 8-12¦Ìm spectral regions. Germanium blocks UV and
visible light and in the infrared up to about 2¦Ìm. Its high index is desirable for the design of lenses that might
not otherwise be possible. Germanium has nearly the highest density of the infrared transmitting materials and
this should be taken into consideration when designing for weight restricted systems. Germanium is subject to
thermal runaway, meaning that the hotter it gets, the more the absorption increases. Pronounced transmission
degradation starts at about 100¡ãC and begins rapidly degrading between 200¡ãC and 300¡ãC, resulting in
possible catastrophic failure of the optic. |
|
| Property |
Specification |
| Transmission Range |
2 to 14¦Ìm |
| Density |
5.33g/cm3 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient |
2.3x10-6 /¡ãK @ 100¡ãK, 5.0x10-6 /¡ãK @ 200¡ãK, 6.0x10-6 /¡ãK @ 300¡ãK |
| Surface Finish |
Typical specifications for surface quality in the infrared are 40-20 or 60-40 scratch
dig in the 2 to 7¦Ìm spectral region and 60-40, 80-50 or 120-80 scratch- dig for the
7-14¦Ìm area, depending upon system performance requirements. |
| Surface Figure |
Surface figure: In the infrared, typical surface figure ranges from 1/2 wave to 2
waves @0.6328¦Ìm depending on the system performance requirements. |
| AR Coating Options |
Typical available coatings for Germanium include BBAR for 3 to 5¦Ìm, 8 to 12¦Ìm,
and the 3 to 12¦Ìm spectral regions. Many application specialized bands are
possible between the 2 and 14¦Ìm. |
| Typical Applications |
Thermal imaging, FLIR. |
| Products Manufactured |
Lenses, Aspheric Lenses, Binary (Diffractive) Lenses, Windows, Optical
Beamsplitters, Optical Filters, Wedges. |
|
|
|
|
|
 Optical
Transmittance Curve of Ge (Reference Data): Optical
Transmittance Curve of Ge (Reference Data): |
|
 |
|
|
|
 Zinc Selenide (ZnSe )------------------------------------- ------- Zinc Selenide (ZnSe )------------------------------------- ------- |
|
|
 Zinc Selenide is used for infrared windows, lenses, and prisms where transmission in the range 0.63¦Ìm to
18¦Ìm is desired. Zinc Selenide has a very low absorption co-efficient and is used extensively for high power Zinc Selenide is used for infrared windows, lenses, and prisms where transmission in the range 0.63¦Ìm to
18¦Ìm is desired. Zinc Selenide has a very low absorption co-efficient and is used extensively for high power
infrared laser optics. It is non-hygroscopic.
Zinc Selenide is a relatively soft material and scratches rather easily. The low absorption of the material avoids
the thermal runaway problems of Germanium. Zinc Selenide requires an anti- reflection coating due to its high
refractive index if high transmission is required. ZnSe has a fairly low dispersion across its useful transmission
range.
Zinc Selenide, a chemically vapor deposited material, is the material of choice for optics used in high power
CO2 laser systems due to its low absorption at 10.6¦Ìm. However it is also a popular choice in systems
operating at various bands within its wide transmission range. ZnSe has a high resistance to thermal shock
making it the prime material for high power CO2 laser systems. ZnSe however is only 2/3 the hardness of ZnS
multi-specral grade but the harder anti-reflectance coatings do serve to protect ZnSe. Zinc Selenide¡¯s cost is
about the same as ZnS multi-spectral grade and is generally more expensive than Germanium. |
|
| Property |
Specification |
| Transmission Range |
0.6¦Ìm to 16¦Ìm |
| Density |
5.27g/cm3 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient |
7.1x10-6 /¡ãK @ 273¡ãK, 7.8x10-6 /¡ãK @ 373¡ãK, 8.3x10-6 /¡ãK @ 473¡ãK |
| Surface Finish |
Typical specifications for surface quality in the infrared are 40-20 or 60-40 scratch
dig in the 0.8 to 7¦Ìm spectral region and 60-40, 80-50 or 120-80 scratch-dig for the
7 to 16¦Ìm area, depending upon system performance requirements. Diamond
Turned surface finishes of 150 Angstroms rms or better are typical. |
| Surface Figure |
In the infrared, typical required surface figures range from 1/2 wave to 2 waves
@0.6328 ¦Ìm depending on the system performance requirements. |
| AR Coating Options |
Typical available coatings for ZnSe include BBAR for 0.8 to 2.5¦Ìm, 3 to 5¦Ìm,
1 to 5¦Ìm, 8 to 12¦Ìm, and the 3 to 12¦Ìm spectral regions and single wavelength
coating AR at 10.6¦Ìm. Many other specialized wavelength bands are possible within
the 0.6 to 16¦Ìm range. |
| Typical Applications |
CO2 laser systems, Thermal imaging, FLIR, Astronomical, Medical |
| Products Manufactured |
Lenses, Aspheric Lenses, Binary (diffractive) Lenses, Windows, Optical
Beamsplitters and Optical Filters, Prism. |
|
|
|
|
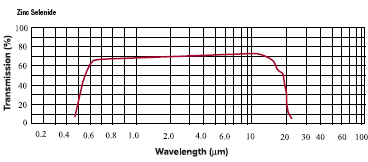
 Optical
Transmittance Curve of ZnSe (Reference Data): Optical
Transmittance Curve of ZnSe (Reference Data): |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 Contact Contact
If you have any questions or comments, please contact us by filling-in the mail form.
|
|
|



